Telemedicine has been aiding healthcare systems in delivering easy and convenient patient care for several years. However, it wasn’t until recently that the concept has exploded to a larger radius. The COVID-19 pandemic has been a pivotal factor accelerating the telehealth trend.
Before the pandemic, numerous barriers to the implementation of telehealth existed. Training healthcare staff on the use of new electronic platforms was seen as a significant challenge to telemedicine adoption across healthcare systems. In addition, there was a general unwillingness among providers to transform their current practices, which had been working sufficiently for years, into a new way of delivering medical care.
With the coronavirus pandemic, adoption of remote healthcare services across the globe has been growing by leaps and bounds. New platforms for delivering teleconsultation, telemonitoring, tele-training, and other servicers are constantly emerging in the market.
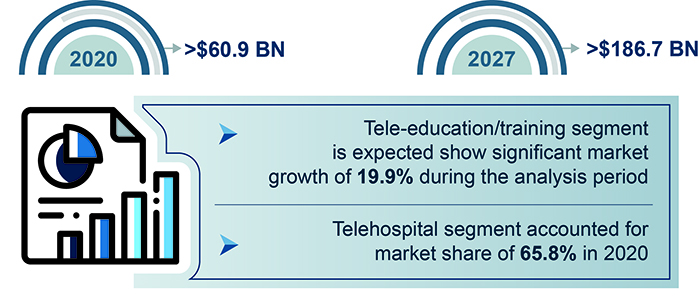
The sustained nature of the COVID-19 pandemic and constant technological innovations could propel global telemedicine market size to more than $186.7 billion by 2027, says Global Market Insights, Inc. American Well, AMD Global Telemedicine, Allscripts Healthcare Solutions Inc, Cisco Systems, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Honeywell International Inc, and Teladoc are currently among the top competitive challengers in the fast-evolving telehealth space.
How Has COVID-19 Fueled the Rise of Telemedicine in the United States?
With an aim to limit contact with potentially infected patients and minimize the spread of the coronavirus in healthcare environments, telehealth has been rapidly integrated into everyday practice. Digital health services are being widely incorporated into inpatient care across hospitals to balance the supply of medical services.
Last year, the CDC analyzed deidentified encounter data from some of the largest telemedicine service providers that operate in all U.S. states, to study trends in telehealth adoption during the early pandemic period. According to the findings, Q1 2020 witnessed a nearly 50% spike in telehealth visits compared to the same period in 2019. A staggering 154% surge was observed in the last week of March 2020 compared to 2019 data.
In March 2020 CMS had widened access to Medicare telemedicine services so that beneficiaries could avail a wider range of healthcare services without having to visit the hospital.
Continuous telehealth policy changes and regulatory waivers will enhance patient access to primary and specialty care during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020, the North American telemedicine industry generated about $36.6 billion in annual revenue, with substantial contribution by the United States.
The 2021 Teleconsulting Boom in Asia Pacific
Teleconsultation services have been in demand throughout the pandemic, providing patients with safe, reliable and convenient access to clinical care. This demand continues to increase as new COVID-19 variants and waves create new challenges for healthcare providers.
A notable uptick in teleconsulting adoption is being witnessed in the Asia Pacific region. In May 2021, Philippines-based telemedicine provider Medgate reported a 170% rise in teleconsultations in the country since the COVID-19 outbreak. The massive surge in teleconsultation uptake came after the company partnered with the Philippines Department of Health and the National Privacy Commission to deliver free telehealth services.
Regulators and telehealth providers in APAC countries are busy ramping up remote health consultation services as demand increases. For instance, July 2021 Singapore-based telehealth providers increased teleconsulting services as more patients continue to seek video consultation.
In June, The Association of Physicians of India (API) collaborated with Abbott to roll out treatment-specific remote consultation recommendations for cardiology, gastroenterology, diabetes and adult immunizations in the country. The two teams aim to introduce solutions across more areas of expertise in the future.
Globally, teleconsulting will continue to be one of the most sought-after telehealth services in the years to come.
Telecardiology (Telemedicine in Cardiology) Gains Traction
Telecardiology serves as an optimum solution for the management of cardiac patients. Key applications of telehealth in cardiology include:
- Telemonitoring of patients with hypertension or chronic heart failure
- Teleconsultation for regular check-ups, follow-ups, and for emergency
- Remote monitoring of patients with implanted cardiac devices
The coronavirus pandemic has disrupted every aspect of cardiovascular care delivery, and healthcare systems must quickly respond to avoid negative effects on patient care and outcomes. The pandemic also gives rise to a significant prospect for implementing telemedicine services for primary and secondary cardiovascular care.
Numerous regulator-approved telemedicine platforms for cardiological care are available on the market. For example, Cardio-HART, a cardiac telemedicine device, obtained CE Mark certification in August 2020, permitting its use in the European Union.
Medical research institutes and organizations are actively making strides to improve access to telecardiology services. In June, the American College of Cardiology and the Heart Rhythm Society, and the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance had partnered to launch the TRANSFORM: AF initiative. Transform is a comprehensive 18-month program to deliver the necessary resources and tools for managing atrial fibrillation using telemedicine, virtual care and remote monitoring.
The Future of the Telemedicine Market
With patients becoming increasingly accustomed to the level of medical access that telemedicine provides, it’s no surprise that the technology is here to stay. It will become an efficient option for preventive care. Patients will choose hospitals, health systems and providers based on telemedicine access. Healthcare facilities that embrace telehealth will likely witness business and revenue growth. As such, the need for cost-effective service delivery in healthcare, adoption of smart devices, and supportive government efforts will propel the telemedicine industry forward in 2021 and beyond.







