A meteoric rise in the diabetic population has made blood glucose monitoring technology a global research topic. It has subsequently sent self-monitoring technologies mainstream, as they proved to be pragmatic and convenient. According to the International Diabetes Federation, more than 460 million adults were living with diabetes in 2019; the number is projected to jump to 700 million by 2045. The WHO estimates that about 422 million people have diabetes across the globe.
Wearable devices such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) products are bringing about a paradigm shift, as more companies adopt the technology. Both healthcare providers and patients are counting on digitally based diabetes management system and virtual care.
Inevitably, self-monitoring has streamlined the use of regular blood testing to assess one’s diabetes control and inform changes to enhance one’s control. With diabetes being related to the body’s ineffective use of insulin, the disease has the legacy of a high incidence rate, wide pathogenic factors, various complications and difficulty in curing and causing other lethal hazards to human health.
Traction for easy-to-use blood glucose devices has become pronounced and is paramount to prevent or detect hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Several technological advances have pushed manufacturers to introduce meters that are less painful and invasive at the time of testing, and can provide robust and rapid testing with alternative-site testing and a smaller sample size.
Type II Diabetes Provides Opportunities
The IDF has emphasized that the proportion of people with type 2 diabetes is soaring in the majority of countries. About 374 million people are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
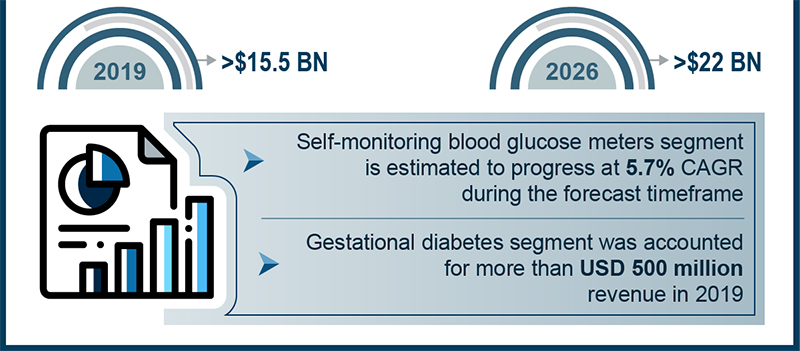
Of late, adults with type 2 diabetes have exhibited increased palpability towards the use of technology to self-monitor health behaviors and lifestyle. To put this in perspective, technology-assisted self-monitoring is perceived as safe and effective in eliciting favorable health outcomes. Global Market Insights, Inc., has projected the self-monitoring blood glucose devices market size to surpass $22 billion by 2026.
Connecting the Dots with CGM Systems
Over the past several years, CGM has become indispensable to monitor blood sugar levels through a wearable device that collates data on glucose levels in the body. A couple of the striking factors of CGM devices include that they do away with the need for finger pricking and enable patients to analyze the data to comprehend patterns and observe trends.
Advancements in glucose self-monitoring technologies have made the monitoring process automated and reliable as the patients can assess and check the glucose levels at any time, and doctors can use the collated data to make informed decisions. Innovations have made devices smaller, more convenient and more reliable; connected, innovative and automated monitors are on the horizon. In addition, CGM technologies are touted to be efficient in reducing hypoglycemia and A1C.
Popular as a means of stick-free glucose testing, CGM devices have gained ground and have a clear edge over contemporary methods for controlling insulin dosage. Companies are gearing up to make strategic moves to bolster their CGM portfolios. For example, last year Tandem Diabetes Care announced the commercial launch of the t: slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology, which integrates with Dexcom G6 CGM.
Following the postponement of its product launch in 2020, Dexcom is contemplating the launch of the G7 CGM system at the end of 2021 with further launches in 2022. The company collaborated with Teladoc Health in January 2021 to provide personalized information to patients with type 2 diabetes.
With real-time synchronization gaining impetus, the advent of CGM technologies has prompted several innovations, product launches and approvals—so much so that the FDA released temporary policies to boost technologies that enable remote patient monitoring of patients with diabetes during COVID-19.
Abbott received the green light from FDA for its FreeStyle Libre diabetes device as an iCGM (integrated continuous glucose monitor) in June 2020. The company also teamed up with Insulet in February 2020 to integrate its CGM technology with the latter’s automated insulin delivery system.
Drawing Upon Key Strategies Via Product Launches and Smart Devices
The outlook for product launches, R&D activities and commercialization of CGM devices has proven to be a watershed moment in the self-monitoring of blood glucose devices landscape. Seamless and personalized diabetes care has become a new normal.
Future trends allude to the use of smartphones as smart devices and have witnessed unprecedented developments in home settings and hospitals. For example, Medtronic launched what it calls the world’s first smart CGM system. The technology will be connected with smartphone displays for real-time data viewing of glucose levels.
In addition, the use of CGM throughout pregnancy may improve glucose control and neonatal outcomes linked with type 1 diabetes in pregnancy, asserts the NHS. With the incidence of diabetes soaring globally, the majority of the devices are being sold to patients with type 1 diabetes. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes and the trend for CGMs among new populations presents massive revenue-boosting opportunities for stakeholders in the self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) devices industry.
Medical technology companies—from corporates to startups—are rethinking strategies and reinventing themselves to gain a hold in the market and empower patients. SMBG devices will remain invaluable in helping healthcare organizations attain better patient results, enhance efficiency and reduce healthcare costs.