
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed a system that mimics humanlike models for studying cardiovascular disease to reduce the reliance on animal testing and shorten drug development timelines.

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed a system that mimics humanlike models for studying cardiovascular disease to reduce the reliance on animal testing and shorten drug development timelines.

A new survey from Frost & Sullivan highlights the key barriers to adoption of real world data and analytics in health care and life sciences.

Vladimir A. Makatsaria, who most recently served as Company Group Chairman at Johnson & Johnson MedTech, leading its global Ethicon surgery business, has been appointed CEO of global medical technology company LivaNova. Former CEO Bill Kozy will serve a Board Chair.

While AI is already making significant contributions to pre-operative planning and post-operative analysis, its utilization intra-operatively remains a key area for further development. Collecting and utilizing comprehensive intra-operative surgical data, as facilitated by innovative applications of existing technologies such as light field, will pave the way for advanced AI applications in spine surgery.
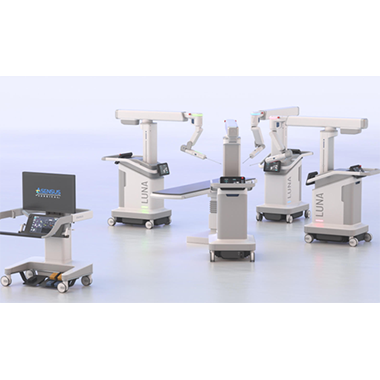
“Flex’s proven track record of delivering complex electromechanical systems across diverse industries and deep understanding of the complex requirements for medical devices will enable us to accelerate time-to-market for our LUNA platform.”

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is seeking input from industry to support its response to President Biden’s Executive Order on AI. Comments, which are due February 2, 2024, will help NIST develop guidelines for evaluation and red-teaming, consensus-based standards and more.

The pilot program launched by Baxter International and Northwestern Medicine in Chicago resulted in the recycling of more than 170,000 IV bags. Baxter is now working to expand the program in the Chicago area to further validate the process and economic viability of the program.

Even AI models trained on general medical literature will have difficulty making sense of the nuances specific to primary care, which is full of unique jargon, abbreviations and other idiosyncrasies. As always, the proverbial devil is in the details. Any AI solution worth its salt must be fluent in the specific idioms of the field and empower clinicians to deliver the best care that they can.

A recent survey by the AMA showed that practicing physicians are equally excited and concerned about the increased use of AI in health care, with enthusiasm for technologies that reduce administrative burden and enhance diagnostic ability and concern for patient privacy, liability and erosion of the patient-physician relationship.

The use of Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology in healthcare, particularly within closed-loop systems, presents complexities, including potential limitations on interoperability that can affect patient safety. Here we look at key challenges including data silos, interoperability barriers, market fragmentation, impediments to innovation and operational inefficiencies.