

Designed to detect drugs of abuse through sweat collected from the fingertips and provide results within ten minutes, the non-invasive test is particularly beneficial in safety-critical industries.

Designed to detect drugs of abuse through sweat collected from the fingertips and provide results within ten minutes, the non-invasive test is particularly beneficial in safety-critical industries.

AI and real-time data enhance care efficiency and access. And with healthcare workers in short supply, the rapid advancements in AI, IoMT, and related innovation offer patient access freedom, enhanced care delivery, and better outcomes.
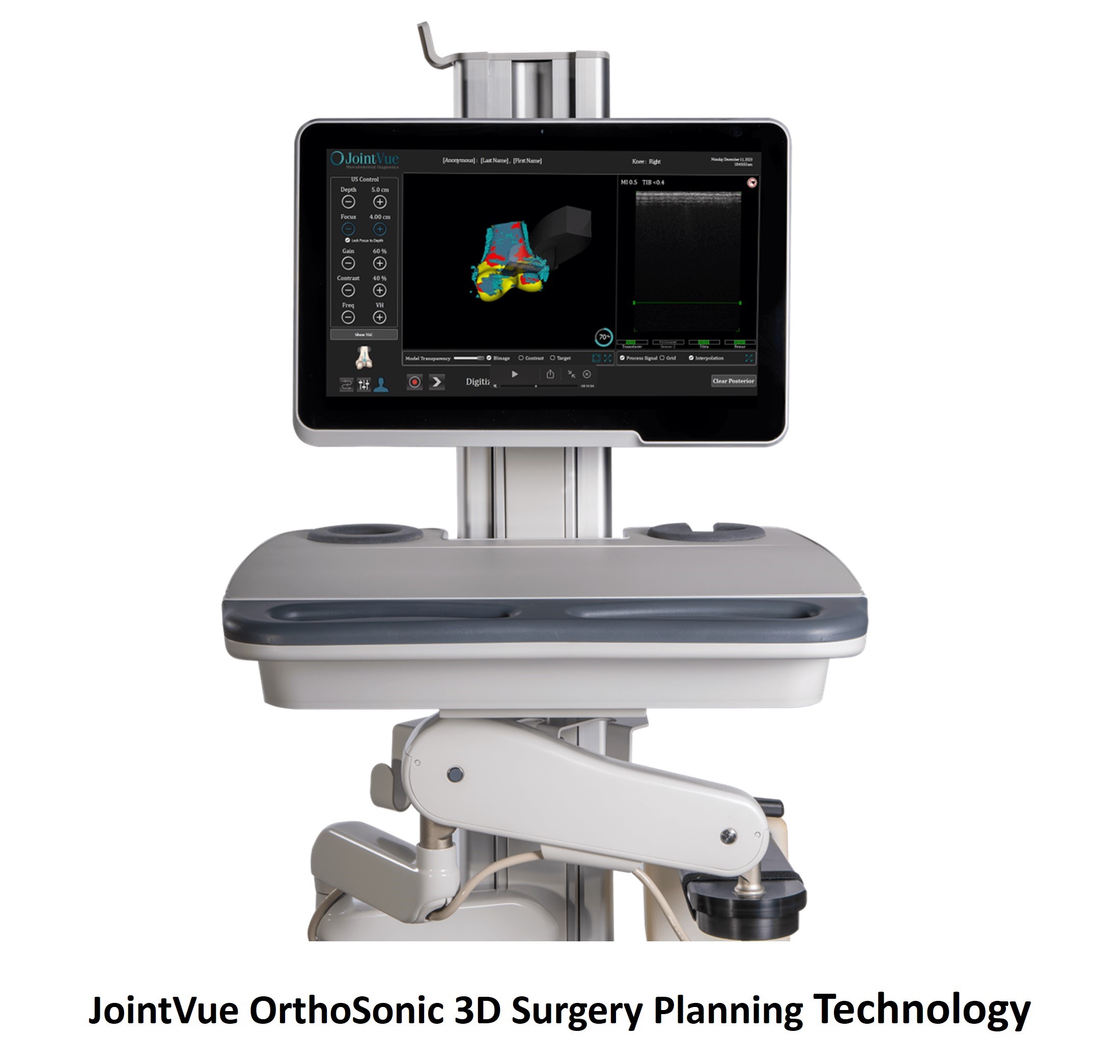
Smith+Nephew and JointVue signed a co-marketing agreement for OrthoSonic 3D surgery planning technology. The technology allows surgeons using the Smith & Nephew Cori surgical robot to create personalized knee arthroplasty procedure plans.

Collaboration tackles complex challenges using data science to improve decision-making in cancer care.
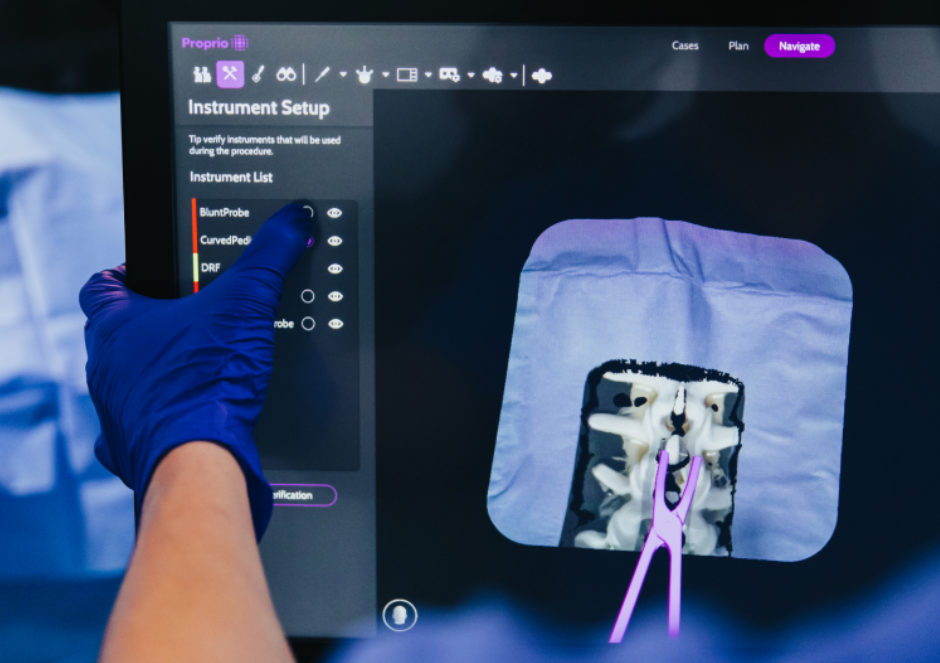
Light field technology is illuminating a path to a deeper understanding of patient anatomy, surgeon methodology, and surgical environments. Traditionally, spine surgery navigation has depended on surgeons combining pre-operative imaging with intra-operative anatomy to execute their treatment plans. However, with light field technology and depth sensors, these technologies digitize the entire operative field, merging it seamlessly with preoperative imaging, effectively bridging the gap between unseen and visible physical anatomy of the spine. This provides surgeons with a three-dimensional anatomical view that exceeds what the naked eye can discern.

Diagnostic manufacturers and pharmaceutical sponsors with therapeutics that rely on biomarker identification or companion diagnostics should adjust their commercialization and partnership strategies to fit the new regulatory environment.

North Carolina healthcare provider supplies clinicians with immediate, on-site access to 3D-printed anatomic models and support through Ricoh Managed Services.

FDA has finalized its landmark proposed rule that will amend the definition of “in vitro diagnostic (IVD) products” in 21 CFR 809.3 to make explicit that IVDs are medical devices under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA), “including when the manufacturer of the IVD is a laboratory.”

San Diego-based medical tech company, Cue Health, announced Monday that it is laying off its entire staff. Similar industry reports indicate a complete shuttering of operations.

Researchers have developed a new machine-learning model that can precisely make prognosis predictions for patients with osteosarcoma, based on the density of viable tumor cells post-treatment.